
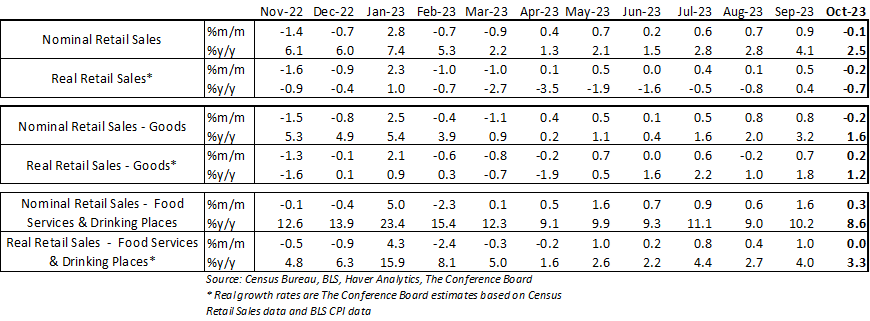
Retail sales fell for the first time since Q1 2023 in October as US consumers pulled back following a spending binge over the summer period. Consumer spending decreased by 0.1% in October, vs. an increase of 0.9% in September, and 0.7% in August. After adjusting for inflation using CPI data, real October spending growth was -0.2% from September*. We expect this pullback in spending to continue and intensify into 2024. Real disposable personal income growth has been stagnant for months and credit card debt and credit card delinquencies are rising rapidly. Pandemic excess savings are likely nearly exhausted at this point and many consumers have resumed paying student loans after a three year pause. These headwinds to consumption coupled with a pullback in business investment associated with decades-high interest rates are likely to tip the economy into contractionary territory in H1 2024. We expect that the NBER will classify this period as a recession. Regarding the drivers of retail sales this month: Consumer demand for goods fell 0.2% from the month prior in nominal terms. Spending on motor vehicles and parts fell by 1.0% in October from September, while retail sales excluding motor vehicles rose by 0.1%. Spending at gasoline stations fell 0.3% from the month prior due to declines in oil prices. Retail sales less motor vehicles, gasoline, and building supplies (known as “Retail Control”) rose by 0.2% from the previous month. Nonstore retail sales rose 0.2% from the month prior. When adjusting goods spending for CPI inflation, the real growth rate was about -0.6%.* Meanwhile, spending at food services and drinking places rose by 0.3% month-over-month in October. After adjusting for CPI inflation the real growth rate was about flat.* * Real growth rates are The Conference Board estimates based on Census Retail Sales data and BLS CPI data.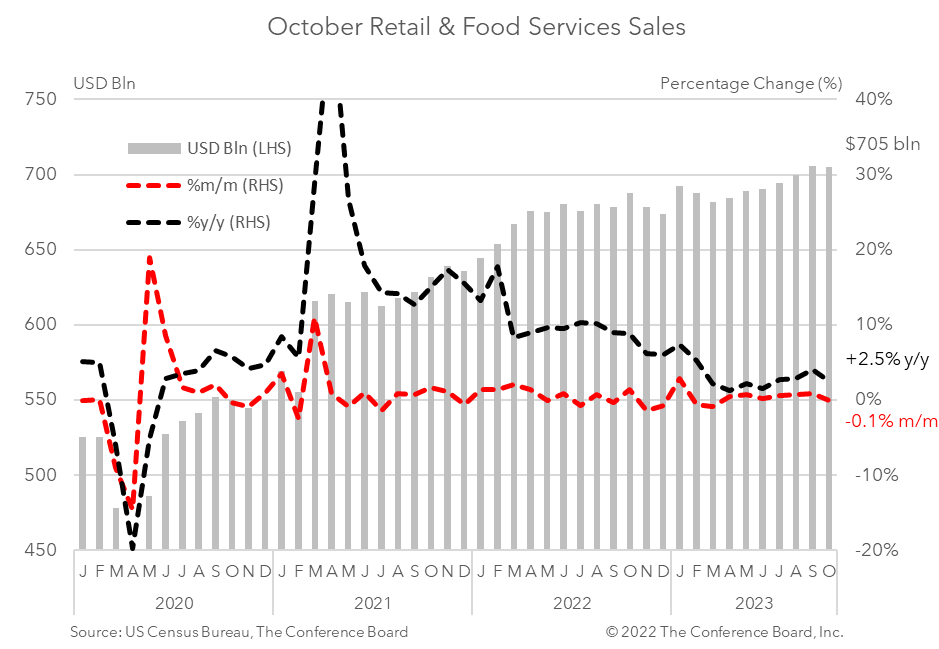
Shutdown Aside, Growth Moderates Under Inflationary Pressures
February 20, 2026
January CPI Raises More Questions than Provides Answers
February 13, 2026
Lukewarm Holiday Shopping in 2025 Augurs Slower Spending in Q4
February 10, 2026
FOMC Reaction: US Economy In a Good Place, But Staying Vigilant
January 28, 2026
Fed January Decision: Pause or Full Stop?
January 27, 2026
November PCE: Are Consumers Spending Beyond Their Means?
January 22, 2026
